Water Treatment
Treatment Process
Cedar Knox Rural Water Project (CKRWP) uses the excess lime treatment process to treat and clarify water pumped from Lewis & Clark Lake. This process softens the raw water to 6 to 8 grains of hardness. The finished water is fluoridated and chlorinated.
CKRWP is required by Nebraska Department of Environment and Energy (NDEE) to comply with water quality standards. Each year NDEE requires publishing the ![]() Consumer Confidence Report which lists CKRWP water test results for the previous year. On January 31st, 2025, Nebraska Department of Environment and Energy (NDEE) issued CKRWP a
Consumer Confidence Report which lists CKRWP water test results for the previous year. On January 31st, 2025, Nebraska Department of Environment and Energy (NDEE) issued CKRWP a ![]() Notice of Violation for Total Trihalomethanes (TTHM) exceeding drinking water standards. Due to this violation CKRWP will be under Administrative Order with NDEE until a permanent solution is implemented. Increased carbon filtration changing the way chlorine is managed has helped decrease TTHM production, however, work continues with engineers to identify additional methods to lower TTHM levels further.
Notice of Violation for Total Trihalomethanes (TTHM) exceeding drinking water standards. Due to this violation CKRWP will be under Administrative Order with NDEE until a permanent solution is implemented. Increased carbon filtration changing the way chlorine is managed has helped decrease TTHM production, however, work continues with engineers to identify additional methods to lower TTHM levels further.
A telemetry system that monitors the treatment process 24 hours a day, 7 days a week allows CKRWP system to be operated by a limited number of personnel. This automated computer system provides the capability to operate and monitor the system from anywhere. CKRWP is required to have at least one Certified Grade II water system operator on staff. All CKRWP operations staff are working towards the necessary certification to attain and/or maintain Grade II certification. In order to obtain and maintain certification, employees are required to attend certification classes, continue to attend operator training classes, and learn current treatment regulations. Cope Clark is a Certified Grade I water system operator, Vince Lammers is a Certified Grade III and VI water system operator, and Scott Fiedler is a Certified Grade II water system operator, with NDEE.
To search water quality test results go to the Public Water Supply Systems Search website.
Treatment Process Diagram
The diagram below details the steps in the treatment process. A brief description of each step in the process is detailed below the diagram
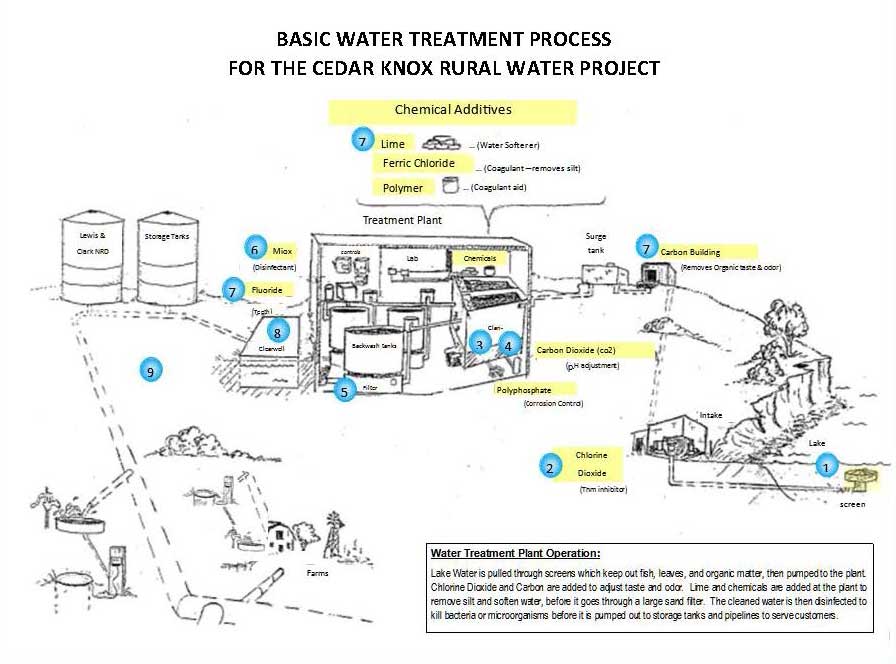
Treatment Process
- Draw Raw Water from Lake to Intake
- Intake: More than 140 million gallons of raw water is drawn from Lewis and Clark Lake annually for treatment. Screens keep out fish, leaves and other organics from entering system.
- Intake: More than 140 million gallons of raw water is drawn from Lewis and Clark Lake annually for treatment. Screens keep out fish, leaves and other organics from entering system.
- Disinfection Pre-Treatment
- Disinfection Pre-Treatment: Chlorine Dioxide is used in the pre-treatment of raw water to effect inactivation of residual pathogens in the final drinking water.
- Disinfection Pre-Treatment: Chlorine Dioxide is used in the pre-treatment of raw water to effect inactivation of residual pathogens in the final drinking water.
- Coagulation
- Coagulation: Removes dirt and other particles suspended in water. Ferric Chloride is added to water to form tiny sticky particles called “floc” which attract the dirt particles. The combined weight of the dirt and the ferric chloride (floc) becomes heavy enough to sink to the bottom for removal during sedimentation.
- Coagulation: Removes dirt and other particles suspended in water. Ferric Chloride is added to water to form tiny sticky particles called “floc” which attract the dirt particles. The combined weight of the dirt and the ferric chloride (floc) becomes heavy enough to sink to the bottom for removal during sedimentation.
- Sedimentation
- Sedimentation: The heavy particles (floc) settle to the bottom for removal and clear water moves to filtration.
- Sedimentation: The heavy particles (floc) settle to the bottom for removal and clear water moves to filtration.
- Filtration
- Filtration: The water passes through filters, made of layers of sand that help remove even smaller particles that remained following sedimentation.
- Filtration: The water passes through filters, made of layers of sand that help remove even smaller particles that remained following sedimentation.
- Disinfection -MIOX Treatment (Chlorination)
- Disinfection: A small amount of Chlorine is added to kill any remaining bacteria or microorganisms that may be in the water.
- Disinfection: A small amount of Chlorine is added to kill any remaining bacteria or microorganisms that may be in the water.
- Additional Treatment
- Fluoride: Helps prevent tooth decay.
- Lime: Clarifies the water & softens raw water to 6-8 grains hardness.
- Carbon Filtration: Improves taste and odor of finished water.
These processes occur at multiple locations during the treatment process.
- Clearwell
- Clearwell: Water is placed in clearwell tanks to allow time for disinfection to take place. The water then flows through pipes to homes and businesses.
- Clearwell: Water is placed in clearwell tanks to allow time for disinfection to take place. The water then flows through pipes to homes and businesses.
- Distribution System
- Distribution System: Consists of 392 miles of pipeline, 3 storage tanks, 2 clearwells, 4 booster stations and 8 pressure reducing stations. Cedar Knox Rural Water has more than 900 service connections which include 4 communities, 3 housing subdivisions and 5 recreation areas.
